Chitin
Chitin
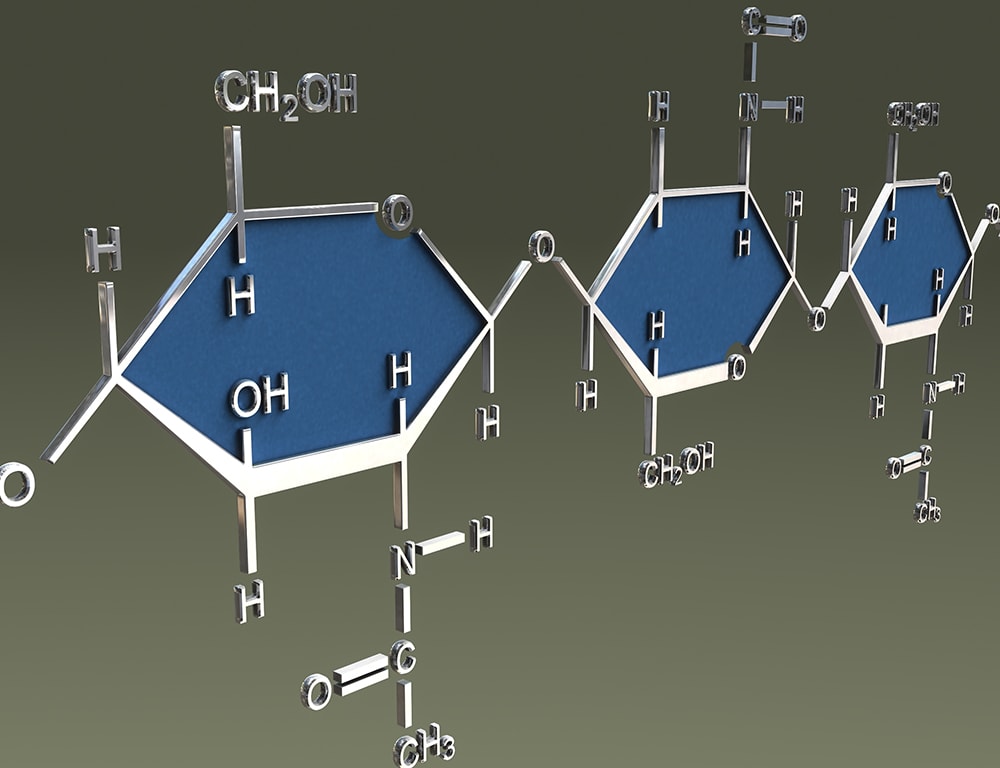
Chitin is a polysaccharide composed from N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units. It is the second most abundant biopolymer on Earth and found mainly in invertebrates, insects, marine diatoms, algae, fungi, and yeasts. Recent investigations confirm the suitability of chitin and its derivatives in chemistry, biotechnology, medicine, veterinary, dentistry, agriculture, food processing, environmental protection, and textile production. The development of technologies based on the utilization of chitin derivatives is caused by their polyelectrolite properties, the presence of reactive functional groups, gel-forming ability, high adsorption capacity, biodegradability and bacteriostatic, and fungistatic and antitumour influence. Chitin is the second most natural polysaccharide after cellulose on earth and is composed of β (1->4)-linked 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucose (N-acetylglucosamine). Chitin is a structural component in crustaceous shells such as shrimp and crab shells and also in squid pen and cell wall of some bacteria and fungi.